What Is DeFi 2.0 and Why It Matters
DeFi 2.0 is more than just the next step in decentralized finance—it’s a response to the real problems in DeFi 1.0. It improves how protocols manage liquidity, reduces risk, and introduces models that work better over time. You’re not just getting higher yields or better tools, you’re getting smarter systems. In this article, you’ll see what DeFi 2.0 is, how it works, what it changes, and what comes next.
What is DeFi 2.0?
DeFi 2.0 is the next phase of decentralized finance. It builds on the foundation of DeFi 1.0 but aims to fix its flaws: while DeFi 1.0 gives you open access to lending, borrowing, and yield farming, it relies heavily on temporary rewards and user-provided liquidity.
Read more: DeFi vs. CeFi.
DeFi 2.0 changes that––or, at least, aims to. In this next generation of decentralized finance, protocols can seek to own their own liquidity and manage treasuries more effectively. You’ll see new models like bonding mechanisms and self-repaying loans. These upgrades make DeFi more sustainable, secure, and scalable.
Think of it like moving from Web2 to Web3. Web2 lets you use services, but Web3 gives you ownership and control. Similarly, DeFi 2.0 shifts control from users providing liquidity to protocols managing it themselves.
The Goal of DeFi 2.0
The main goal of DeFi 2.0 is to create a more sustainable and efficient decentralized finance ecosystem. Early DeFi platforms showed what was possible, but they also exposed major weaknesses—fragile liquidity, unsustainable incentives, and high risks.
DeFi 2.0 aims to fix these problems by making the system less dependent on external rewards and more focused on long-term value. Protocols now take ownership of liquidity instead of renting it, which reduces volatility and improves capital efficiency.

The technology’s aim is to make the DeFi ecosystem more secure, scalable, and resilient. You get tools that are easier to use and less risky. Projects build in mechanisms that automatically manage treasuries, adjust incentives, and support growth without constant user input.
In short, DeFi 2.0 doesn’t just upgrade the tech—it upgrades the economics behind decentralized finance.
From DeFi 1.0 to DeFi 2.0
Let’s take a closer look at how DeFi has evolved. DeFi 1.0 proved that decentralized finance could work, but it also came with real trade-offs. DeFi 2.0 steps in to solve those issues.
Limitations of DeFi 1.0
Impermanent loss
When you provide liquidity to a pool, your assets can shift in value compared to if you’re simply holding them. This is called impermanent loss. It’s common in volatile pairs and discourages participation. Many users end up with less value than they put in, even after earning fees.
Liquidity mining drawbacks
Early DeFi platforms grew fast by offering tokens as rewards for liquidity. This worked—at first. But once the rewards stopped, the liquidity vanished and it became a short-term game. Protocols can’t always rely on users to stick around, which leads to instability.
Unsustainable APYs
Some platforms promised eye-popping annual percentage yields (APYs). You saw numbers like 10,000%—sometimes even more. However, these returns weren’t real. They depended on new users constantly entering the system: and once growth slowed, returns crashed and token prices followed.
Overdependence on external incentives
DeFi 1.0 relies too much on short-term bribes. Many protocols can’t control their liquidity or capital. Instead, they rent it from users through rewards, which creates fragile ecosystems, vulnerable to market shocks and token dumps.
Advancements in DeFi 2.0
Introduction of bonding mechanisms
DeFi 2.0 introduces bonding as an alternative to yield farming. Instead of offering tokens for temporary liquidity, protocols let you sell assets (like stablecoins or LP tokens) to the treasury at a discount. In return, you receive the native token over time. This aligns incentives and helps the protocol grow more sustainably.
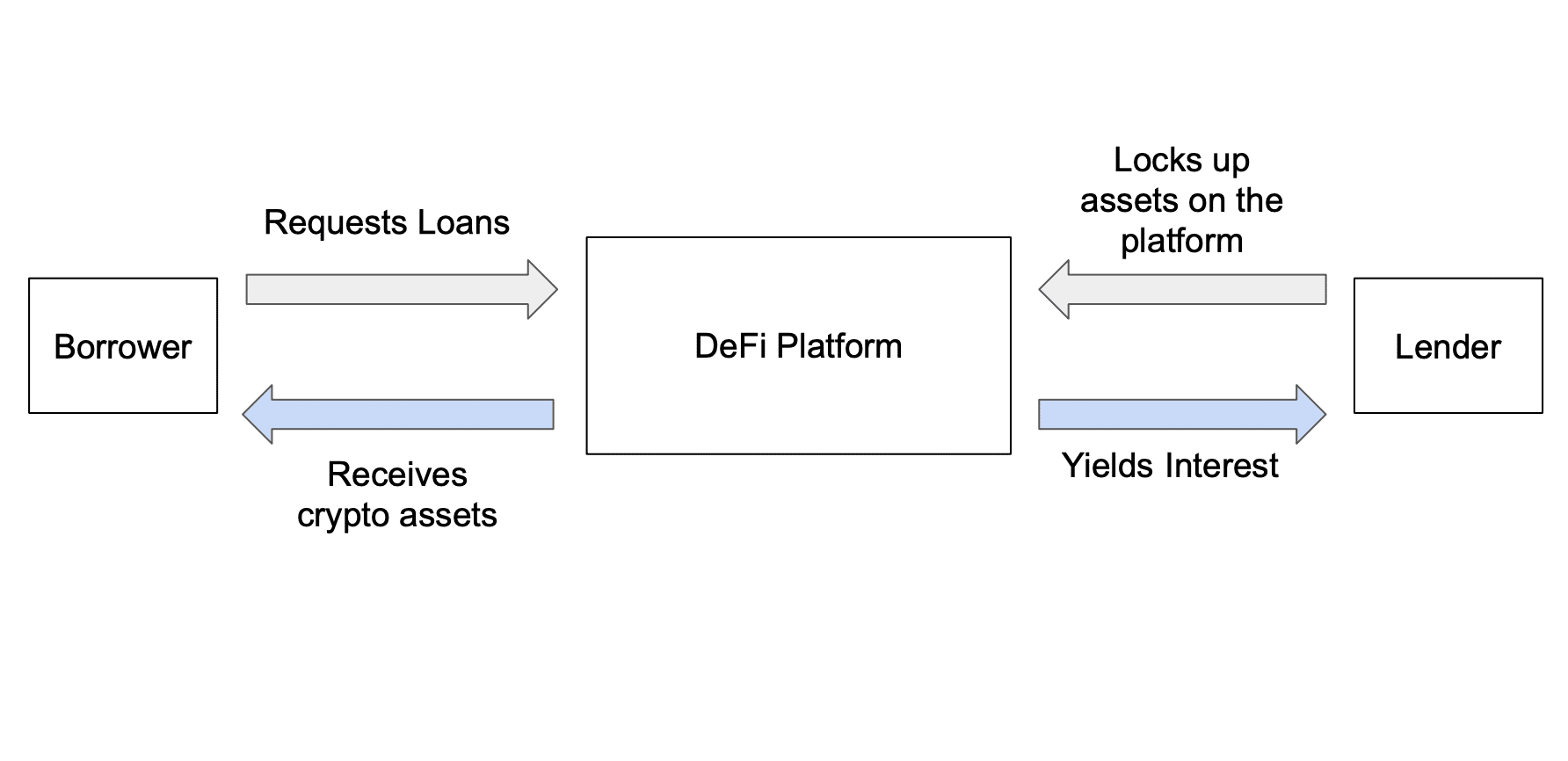
Protocol-owned liquidity (POL)
With POL, platforms no longer depend on user-supplied liquidity. They own it. This creates a stable base for trading and treasury management. OlympusDAO pioneered this approach, reducing volatility and giving protocols more control.
Better treasury management
Treasuries in DeFi 2.0 aren’t idle—they’re strategic. Funds are deployed carefully to support the protocol’s goals. Some platforms even automate treasury operations using smart contracts. This improves transparency, efficiency, and financial planning.
Read more: What are smart contracts?
Core Innovations in DeFi 2.0
But that’s not all––there’s even more to DeFi 2.0. Decentralized finance 2.0 introduces practical upgrades, making DeFi protocols more efficient, sustainable, and resilient. While DeFi 1.0 focused on access, DeFi 2.0 is about control, ownership, and optimization.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the key innovations this new technology can bring to the DeFi projects we know and love.
Improved Scalability
Scalability has always limited the reach of decentralized lending and decentralized exchanges. High gas fees and slow confirmation times made it hard for users and liquidity providers to operate cost-effectively.
DeFi 2.0 solves this with layer-2 solutions like Optimism and Arbitrum, as well as cross-chain deployments on Avalanche, Polygon, and BNB Chain. These platforms offer enhanced liquidity solutions by increasing transaction throughput and reducing costs, making liquidity pools more accessible and functional for you.
Become the smartest crypto enthusiast in the room
Get the top 50 crypto definitions you need to know in the industry for free

Enhanced Security
With DeFi 2.0, you can get real-time threat detection and automated responses. Leading DeFi projects deploy formal verification, bug bounty programs, and on-chain monitoring to detect exploits before they occur.
Protocols like Aave and Compound use multi-signature wallets and governance controls to reduce single points of failure. These safeguards bring DeFi protocols closer to the risk management frameworks of traditional financial systems, except without centralization.
DAO Governance
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) have matured. They aren’t just governance gimmicks, they’re powerful tools. Through DAOs, you can vote on everything from liquidity mining incentives to protocol upgrades and treasury strategies.
Curve, MakerDAO, and Lido are examples of systems where your vote has real influence. This allows liquidity providers and stakeholders to shape the direction of the ecosystem without needing intermediaries.
Read more: What is a DAO?
Cross-Chain Interoperability
DeFi 2.0 embraces a multi-chain future. Through interoperability layers like LayerZero and bridges like Wormhole, protocols enable assets and data to move freely between chains.
This isn’t just a convenience—it ensures sufficient liquidity across ecosystems. You get better trading opportunities and seamless access to decentralized exchanges, regardless of which network you’re using.
Improved User Experience
In DeFi 2.0, there are tools that can unify tracking, investing, and yield farming into a single dashboard. Wallet integrations are also smoother. Some platforms offer gasless transactions, and onboarding flows are simplified.
Automated Treasury Management
Treasury systems are no longer passive. DeFi 2.0 platforms like OlympusDAO and Frax use automated treasury management to optimize capital deployment. They use smart contracts to allocate assets based on market conditions and strategic priorities. This gives protocols more control over liquidity while reducing risk and human error—providing consistent returns to liquidity providers and stabilizing operations.
Yield Farming 2.0
Forget unsustainable APYs. Yield farming in DeFi 2.0 introduces models like bonding, staking with vesting, and protocol-owned liquidity. These approaches replace liquidity incentives with mechanisms that align interests between users and platforms.
Instead of farming and dumping, you now participate in systems designed to generate long-term value. This evolution boosts DeFi protocol resilience and discourages volatility.
Concentrated Liquidity & Dynamic Fees
Uniswap v3 pioneered concentrated liquidity, letting liquidity providers define specific price ranges for asset exposure. This results in higher capital efficiency and deeper liquidity pools for traders.
Dynamic fee models adjust transaction costs in real time, balancing supply and demand. These innovations reduce slippage and front-running, and improve profitability across decentralized exchanges.
Comparative Analysis: DeFi 1.0 vs. DeFi 2.0
DeFi 2.0 isn’t just an upgrade, but a shift in how protocols handle liquidity, governance, and risk. By focusing on sustainability and efficiency, it solves many of the structural issues that held back DeFi 1.0. Here’s a direct comparison between the two:
Security and Risk Mitigation
Unlike traditional institutions, which operate under strict regulations, DeFi operates on open protocols. This freedom brings innovation, but also exposes the DeFi ecosystem to new vulnerabilities.
To support broader adoption, DeFi 2.0 improves security across the board. You’ll see advancements in smart contract safety, risk modeling, and decentralized application infrastructure. These upgrades reduce dependence on external liquidity providers and move DeFi closer to a state of higher efficiency.
Insurance Models
Insurance in DeFi 2.0 protects against smart contract vulnerabilities, hacks, and exploit losses. Protocols like Nexus Mutual and InsurAce offer coverage tailored for decentralized lending platforms, liquidity providers, and DAO treasuries.
You can purchase policies directly within decentralized applications, shielding yourself from protocol-specific risks. This makes participation safer for individuals and institutions.
On-Chain Monitoring
Real-time analytics tools help prevent and respond to attacks. Some DeFi protocols can now continuously scan smart contracts and on-chain behavior to detect anomalies before they become threats.
These systems act as a decentralized security grid—alerting teams, freezing functions, or triggering automated defenses. On-chain monitoring brings DeFi closer to the internal audit capabilities of the more traditional institutions.
Treasury-Backed Risk Coverage
Some DeFi 2.0 projects use their own funds, called treasuries, to help protect users from losses. Instead of depending on outside help, they set aside money to cover problems like token crashes or bugs. This makes the system more stable and shows users that the project takes their safety seriously. It also helps the project stay strong in the long run without needing outside bailouts.
Auditing Improvements
DeFi 2.0 treats audits as an ongoing process—not a checkbox. Projects use multiple independent auditors, run formal verification, and adopt bug bounty programs to crowdsource vulnerability detection.
Protocols like Aave and Compound also maintain transparent GitHub repositories, so you can track changes and review code. This level of openness strengthens the DeFi ecosystem and encourages adoption from risk-conscious users.
Challenges and Considerations
DeFi 2.0 solves many legacy issues, but it’s not without its own set of risks. As the ecosystem grows, new challenges emerge—especially for decentralized applications and the users relying on them.
To achieve broader adoption, DeFi must overcome usability hurdles, complex tokenomics, and regulatory pressure. It also needs to create unified liquidity pools and reduce its fragmentation. Let’s look at the key challenges still facing this efficient financial ecosystem.
Usability and Education Barriers
Even with improved interfaces, DeFi still feels foreign to most users. Wallet setup, bridging, gas fees—these can be overwhelming for newcomers.
Unlike traditional financial institutions where onboarding is streamlined, DeFi often requires you to understand protocols at the code level. Until education improves, and onboarding becomes seamless, adoption will remain niche.
Tokenomics Complexity and Model Abuse
DeFi 2.0 projects often use advanced incentive models to drive behavior. But these systems can be exploited.
Some protocols introduce complex tokenomics that are hard to audit or understand. Users get confused, and bad actors take advantage of loopholes. If projects don’t simplify and clarify value flows, confidence in DeFi platforms may erode.
Market Manipulation and Whale Games
With limited regulation, whales often dominate markets. Large holders can exploit thin liquidity, game yield farming incentives, and manipulate prices across unified liquidity pools.
This kind of behavior damages trust. Until there are on-chain protections or governance limits in place, DeFi projects will remain exposed to manipulation.
Ecosystem Fragmentation
DeFi spans dozens of chains and platforms. Without cross-chain interoperability, liquidity is siloed, and users must constantly bridge assets and manage wallets.
This fragmentation hurts user experience and limits capital efficiency. Protocols need to create truly unified liquidity pools that allow seamless asset flow across the DeFi ecosystem, without the friction of multiple steps.
Legal Grey Areas and Compliance Risks
Regulatory uncertainty is one of DeFi’s biggest risks. Most DeFi platforms operate without clear jurisdiction, exposing them and users to legal ambiguity.
Governments are watching. As regulators consider whether DeFi should follow the same rules as traditional financial institutions, many projects may face enforcement or be forced to change their models. This could impact your access, your funds, or the protocol’s entire structure.
Some Notable DeFi 2.0 Projects
DeFi 2.0 isn’t just about theory, it’s actually being built in real time. A new wave of protocols is already implementing the core ideas of sustainability, user ownership, and efficiency. Here are some of them.
OlympusDAO: Redefining Liquidity
OlympusDAO pioneered the concept of protocol-owned liquidity (POL), allowing the protocol to control its own liquidity rather than relying on external providers. This approach has influenced many DeFi projects aiming for sustainable liquidity models.
Tokemak: Liquidity as a Service
Tokemak offers a decentralized liquidity marketplace, enabling protocols to efficiently direct and manage their liquidity across various exchanges. Its innovative approach has positioned it as a key player in DeFi liquidity provisioning.
Alchemix: Self-Repaying Loans
Alchemix allows users to obtain loans that repay themselves over time by leveraging the yield generated from deposited collateral. This model offers a novel approach to borrowing in DeFi, combining yield farming with lending.
Abracadabra Money: Composability of Interest-Bearing Assets
Abracadabra Money enables users to deposit interest-bearing tokens as collateral to mint its stablecoin, Magic Internet Money (MIM). This allows for increased composability and capital efficiency in the DeFi ecosystem.
Rari Capital: Capital Efficiency Through DAO Strategies
Rari Capital provided a platform for creating customized lending markets through its Fuse protocol. Despite its innovative approach, the platform faced challenges, including a significant exploit in 2022, leading to its eventual discontinuation.
The Future of DeFi: Will There Be a DeFi 3.0?
Yes, you can expect a DeFi 3.0. And it won’t be just a marketing buzzword—it will be (or, at least, we hope so) a real shift in how DeFi works.
DeFi 2.0 solved some major problems: temporary rewards, unstable liquidity, and poor risk controls. But there are still gaps.
1. Real-world assets (RWAs)
DeFi is beginning to tokenize assets like real estate, debt, and commodities. This gives you exposure to markets that used to be off-chain. It also attracts users who want more stable returns. Projects like Golden Pact are already working on this.
2. AI-driven protocols
AI is being tested in risk models, trading bots, and even treasury management. Protocols can now adjust strategies faster than humans can react. This improves efficiency and lowers risks.
3. Better cross-chain tools
You’ll see more interoperability solutions that let you move assets between chains without bridges. LayerZero, Wormhole, and others are working on unified messaging layers to do this.
4. Regulation
Governments are stepping in. The EU’s MiCA framework and US policy proposals are shaping how DeFi can legally operate. This means protocols might have to offer KYC/AML tools or risk being banned from key markets.
5. Liquidity without renting
Expect new systems to replace traditional liquidity mining. Protocols are testing models that offer direct liquidity provisioning, profit-sharing models, or use DAO votes to allocate capital—without farming and dumping.
DeFi 3.0 won’t erase DeFi 2.0. It will extend it. You’ll get smarter automation, access to more markets, and better tools for managing risk—all while staying decentralized.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.
The post What Is DeFi 2.0 and Why It Matters appeared first on Cryptocurrency News & Trading Tips – Crypto Blog by Changelly.
Cryptocurrency News & Trading Tips – Crypto Blog by Changelly

















