What Are Liquidity Pools? A Beginner’s Guide
Have you ever traded crypto on a decentralized exchange and wondered where the tokens come from? Well, the answer lies in liquidity pools. But what are liquidity pools, exactly?
They are the engine behind most DeFi protocols, quietly enabling millions of token swaps every day. By locking digital assets into smart contracts, liquidity pools remove the need for traditional order books and middlemen. They let anyone, anywhere, trade instantly—and give some users the chance to earn passive income by providing the liquidity others rely on. This guide will walk you through how liquidity pools work, why they matter, and how you can start using them.
What Is a Liquidity Pool?
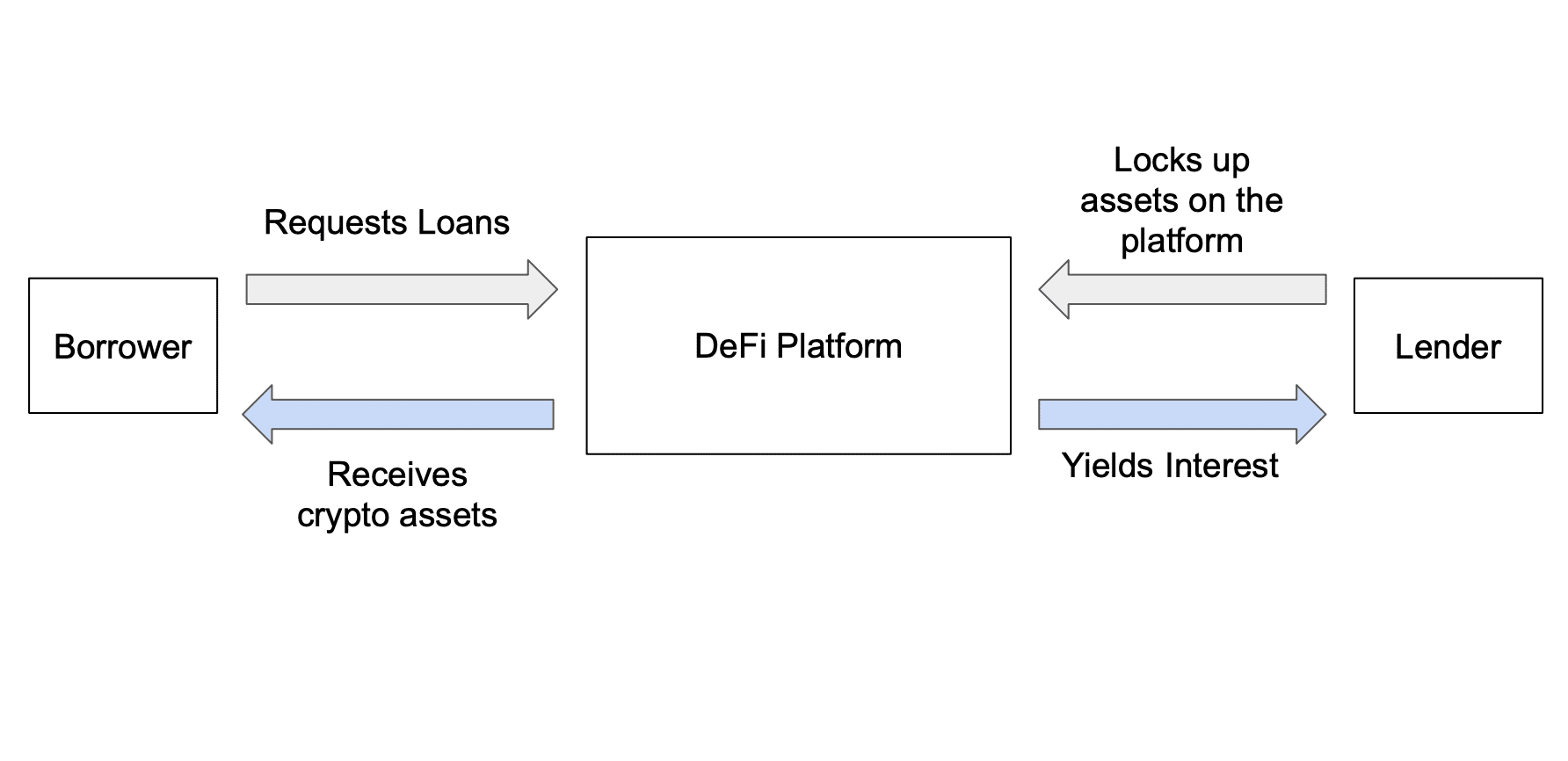
A liquidity pool is a digital collection of cryptocurrency locked in a smart contract. It’s used to enable trading on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap or Curve, where there’s no middleman to match buyers and sellers.
Think of a liquidity pool like a vending machine. You stock it with snacks (cryptocurrencies) so people can come by and make trades. The more snacks available, the smoother the process. In this setup, liquidity providers are the ones who stock the machine. They provide liquidity by depositing two types of tokens into a pool—for example, ETH and USDC.
When someone makes a trade using the pool, they pay trading fees. These fees go directly to the liquidity providers as a reward. This system keeps the pool filled and functioning.
Liquidity pools are essential in decentralized finance (DeFi). Since there’s no centralized order book or market maker, the pool itself allows users to swap tokens instantly. That’s what makes decentralized exchanges work without needing a traditional broker.
Read more: Decentralized vs. centralized exchanges.
What Is The Purpose of a Liquidity Pool?
A liquidity pool ensures that you can trade crypto anytime without needing a buyer or seller on the other side. It keeps markets liquid, even when activity is low, and prevents price slippage during trades. In return for providing liquidity, users earn rewards like trading fees and incentives. This creates a self-sustaining system that fuels nearly every part of the DeFi ecosystem.
These pools also enable automated pricing through algorithms, replacing human market makers. This allows decentralized exchanges to function without centralized control.
Beyond trading, liquidity pools power key DeFi services like lending, yield farming, synthetic assets, and cross-chain bridges. They hold and distribute value automatically based on smart contracts.
How Liquidity Pools Work
Liquidity pools power decentralized trading by removing the need for traditional buyers and sellers. Instead of waiting for someone to match your order, you trade directly against a pool of tokens locked in a smart contract. Let’s take a look at how crypto liquidity pools work.

Token Pairs & Pool Creation
Every liquidity pool starts with a trading pair. This is a combination of two tokens that users can swap between—for example, ETH and USDC. You, as a liquidity provider, deposit equal values of both tokens into the pool. This process is called liquidity provision.
Once the pool is created, users can start swapping one token for another. The pool holds the reserves and executes trades automatically using smart contracts. No centralized entity or order book is involved.
Liquidity Providers (LPs)
Liquidity providers (LPs) are users who fund these pools with their tokens. When you provide liquidity, you receive LP tokens in return. These represent your share in the pool and give you the right to claim a portion of the trading fees.
As trades happen, the pool charges a small fee—often around 0.3%. This fee is distributed among LPs in proportion to their contribution. This is one of the primary ways to earn passive income in decentralized finance.
Some platforms also offer extra incentives through liquidity mining. This means you earn additional tokens—often the platform’s native cryptocurrency—on top of trading fees.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
At the core of every liquidity pool is an Automated Market Maker (AMM). This is the algorithm that sets token prices inside the pool. It replaces the need for human market makers.
The most common AMM model is the constant product formula:
x * y = k, where x and y are token reserves and k is constant. This ensures that the product of the token balances remains the same after every trade.
When you trade in the pool, the AMM adjusts prices automatically. The more you try to buy, the higher the price goes—this mechanism is what enables real-time price discovery.
Earning from Fees & Incentives
Every time someone uses the pool, they pay a trading fee. These fees go directly to LPs. The more trading volume, the more income you earn. On popular platforms like Uniswap, these fees can accumulate quickly.
In addition to fees, many DeFi platforms offer liquidity mining programs. These are incentives paid in extra tokens to attract more liquidity. You can stake your LP tokens to earn rewards, boosting your total returns.
By combining trading fees and incentive rewards, liquidity pools become a powerful tool for generating passive income in DeFi. But you must also consider risks like impermanent loss, which are covered later in the article.
Types of Liquidity Pools
Not all liquidity pools serve the same purpose—here are the main types.

Product Pools
Product pools are the most common type. They allow you to swap one token for another based on market demand. These pools usually follow the traditional automated market maker (AMM) model, such as the constant product formula used by Uniswap. You’ll often find trading pairs like ETH/USDC, WBTC/DAI, or other token combinations. These pools exist primarily to support token trading without centralized intermediaries. They are the backbone of decentralized exchanges.
Because these pools support a wide range of tokens, they can experience higher price volatility, especially in illiquid markets. You earn fees from every trade, but you’re also exposed to impermanent loss if prices shift significantly.
Stablecoin Pools
Stablecoin pools consist of tokens that are designed to maintain a fixed value, usually pegged to fiat currencies like the US dollar. Examples include USDC, DAI, and USDT. These pools use optimized AMMs like Curve’s StableSwap algorithm, which allows low-slippage trades. The reduced volatility makes stablecoin pools ideal for minimizing impermanent loss.
This type of pool is also essential in cross-platform lending protocols, collateral swaps, and yield farming strategies. As prices don’t fluctuate much, they are often considered safer entry points for new liquidity providers.
Smart Pools
Smart pools are programmable liquidity pools governed by smart contracts. Unlike regular pools, smart pools allow custom parameters—such as dynamic weights, automated rebalancing, or time-based rewards. Platforms like Balancer support smart pools, where you can define how much of each token to hold or how the pool should react to market changes. This flexibility attracts advanced users and algorithmic traders.
Smart pools are ideal when you need precise control over how decentralized liquidity is managed. However, they require a solid understanding of smart contract logic to avoid unexpected outcomes.
Lending Pools
Lending pools are used in decentralized lending protocols like Aave or Compound. These pools don’t support direct token swaps. Instead, users deposit assets so others can borrow them, usually overcollateralized.
You earn passive income from interest paid by borrowers. The pool automatically adjusts interest rates based on supply and demand. If there’s high demand to borrow an asset, interest rates increase, encouraging more deposits. These pools are essential in DeFi’s credit layer. They offer a decentralized alternative to traditional banking, without intermediaries. But they also carry risks if collateral values drop too fast during market volatility.
Algorithmic Pools
Algorithmic pools use dynamic models to manage liquidity and pricing. Unlike fixed-formula AMMs, these pools adapt in real time to market conditions.
Bancor’s v3 protocol and Curve’s metapools are examples. They can reweigh assets, rebalance portfolios, or adjust fee structures based on usage data.
Algorithmic pools are ideal for managing illiquid markets, where token prices can swing dramatically. These pools help reduce slippage and improve efficiency. However, the complexity of the algorithms means more technical risk, especially if the code contains bugs or exploits.
Key Benefits of Liquidity Pools
- Decentralized trading access. You can swap tokens without relying on centralized exchanges or third parties.
- 24/7 market liquidity. Liquidity pools allow you to trade anytime, even during low market activity.
- Passive income generation. As a liquidity provider, you earn from trading fees and incentives from every transaction in the pool.
- Permissionless participation. Anyone can create or join a liquidity pool without going through an approval process.
- Reduced reliance on order books. Automated market makers (AMMs) handle pricing and trading, removing the need for matching buyers and sellers.
- Supports DeFi infrastructure. Pools are essential for decentralized lending, borrowing, synthetic assets, and cross-chain swaps.
- Incentivizes ecosystem growth. Liquidity mining and token rewards attract users and help new protocols grow faster.
- Efficient price discovery. AMM algorithms respond instantly to market demand, keeping prices up-to-date.
Become the smartest crypto enthusiast in the room
Get the top 50 crypto definitions you need to know in the industry for free

Risks and Challenges
Liquidity pools carry certain risks that could impact your returns. The most common is impermanent loss, which happens when token prices shift, reducing the value of your deposit compared to simply holding the assets. Smart contract bugs are another danger. If the pool’s code is flawed or exploited, your funds can be lost permanently. Smaller pools also face low liquidity, making trades inefficient and increasing slippage.
Rug pulls are a real threat in unaudited projects, where developers can withdraw funds and disappear. Regulatory uncertainty adds more risk, as changing laws may affect how and where you can use DeFi platforms.
You might also face price manipulation in low-volume pools, especially through flash loans. On top of that, gas fees can be high during busy network periods, making participation costly. For new users, the complexity of these systems can lead to costly mistakes.
Popular DeFi Platforms That Use Liquidity Pools
- Uniswap. A leading decentralized exchange using automated market makers for token swaps.
- Curve Finance. Optimized for stablecoin trading with minimal slippage.
- Balancer. Allows customizable smart pools with flexible token ratios.
- SushiSwap. Community-driven DEX offering yield farming and liquidity incentives.
- Bancor. Features single-sided staking and built-in impermanent loss protection.
Yield Farming and Liquidity Pools
Yield farming is a way to earn extra rewards on top of the fees you already earn from providing liquidity. When you deposit tokens into a liquidity pool, you receive LP (liquidity provider) tokens. Some platforms let you stake those LP tokens in a yield farm to earn bonus tokens—often the platform’s native asset.
This system encourages more users to add liquidity, which keeps pools deep and trading smooth. In return, protocols reward you for helping the ecosystem function.
Yield farming is directly tied to liquidity pools—it’s simply the next step after becoming a liquidity provider. But with higher rewards come higher risks, including impermanent loss and smart contract bugs. Always research before participating.
How To Participate in Liquidity Pools
Getting started with liquidity pools is simple. Follow these steps to join and start earning rewards:
1. Choose a DeFi platform
Pick a reliable platform like Uniswap, Curve, or Balancer. Look for projects with good liquidity, active users, and clear documentation.
2. Connect your wallet
Use a crypto wallet like MetaMask or Trust Wallet. Make sure it supports the blockchain where the pool is hosted (e.g., Ethereum, Arbitrum, or BNB Chain).
3. Select a trading pair
Find a pool you want to join. Most pools require you to deposit two tokens in equal value—like ETH and USDC.
4. Add your tokens
Deposit both tokens into the pool. The platform will calculate the exact amounts you need. After depositing, you’ll receive LP tokens that represent your share in the pool.
5. Stake your LP tokens (optional)
Some platforms let you stake your LP tokens in a yield farm to earn extra rewards. This step is optional but can increase your returns.
6. Earn fees and rewards
As trades happen in the pool, you earn a share of the trading fees. If you’re staking LP tokens, you’ll also receive farming incentives.
7. Withdraw anytime
You can exit the pool whenever you want. Just return your LP tokens to the platform, and you’ll get back your share of the pool—plus any earnings.
Before joining, always check the risks and understand how the specific pool works. Choose well-established platforms to avoid scams or security issues.
Final Thoughts: Is Providing Liquidity Right for You?
Liquidity pools open the door to decentralized income, faster trades, and a new kind of financial freedom. They let you move beyond traditional markets and participate directly in systems that facilitate transactions without banks or brokers. But with greater control comes greater responsibility—and risk.
If you’re comfortable with crypto, understand the risks, and want to earn from your digital assets, providing liquidity might be right for you. Just start small, use trusted platforms, and always stay informed. In DeFi, knowledge is as valuable as capital.
FAQ
How do you make money from a liquidity pool?
You earn a share of the trading fees every time users facilitate trades using the pool. Some platforms also reward you with governance tokens, increasing your profit through yield farming.
What is better, a staking or liquidity pool?
Liquidity pools offer rewards from trading fees and farming, while staking usually pays fixed returns from locking tokens. If you’re looking to facilitate transactions and earn actively, pools may offer higher returns—but with more risk than staking.
Can you take money out of a liquidity pool?
Yes, you can withdraw your share at any time by redeeming your LP tokens. The smart contract returns both your assets, plus any earned fees, minus any potential impermanent loss.
Can you lose crypto in a liquidity pool?
Yes, you can lose value due to impermanent loss, smart contract bugs, or scams. Unlike traditional markets, there’s often no insurance or recovery if something goes wrong.
What assets are in a liquidity pool?
Most pools hold two digital assets like ETH and USDC. Some advanced pools may include multiple tokens and use algorithmic strategies to balance and manage liquidity.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.
The post What Are Liquidity Pools? A Beginner’s Guide appeared first on Cryptocurrency News & Trading Tips – Crypto Blog by Changelly.
Cryptocurrency News & Trading Tips – Crypto Blog by Changelly



















