What Is Polkadot (DOT)? The Blockchain That Connects Blockchains
The crypto invention didn’t stop at one blockchain. It exploded into multiple blockchains that rarely talk to each other.
Polkadot was built to fix that. It connects different chains under one network with shared security and coordination. Here’s a simple, no-nonsense look at what Polkadot does and why people care.
What Is Polkadot (DOT)?
Polkadot is a blockchain platform that connects different blockchains into one shared network. Instead of running as a single chain, it allows many blockchains to work together. In simple terms, Polkadot lets blockchains communicate and coordinate instead of operating in isolation. This design helps blockchains share data, stay secure, and scale without congestion.
The name Polkadot refers to both the technology and the live Polkadot network.
The native cryptocurrency of Polkadot is DOT, also called DOT tokens.
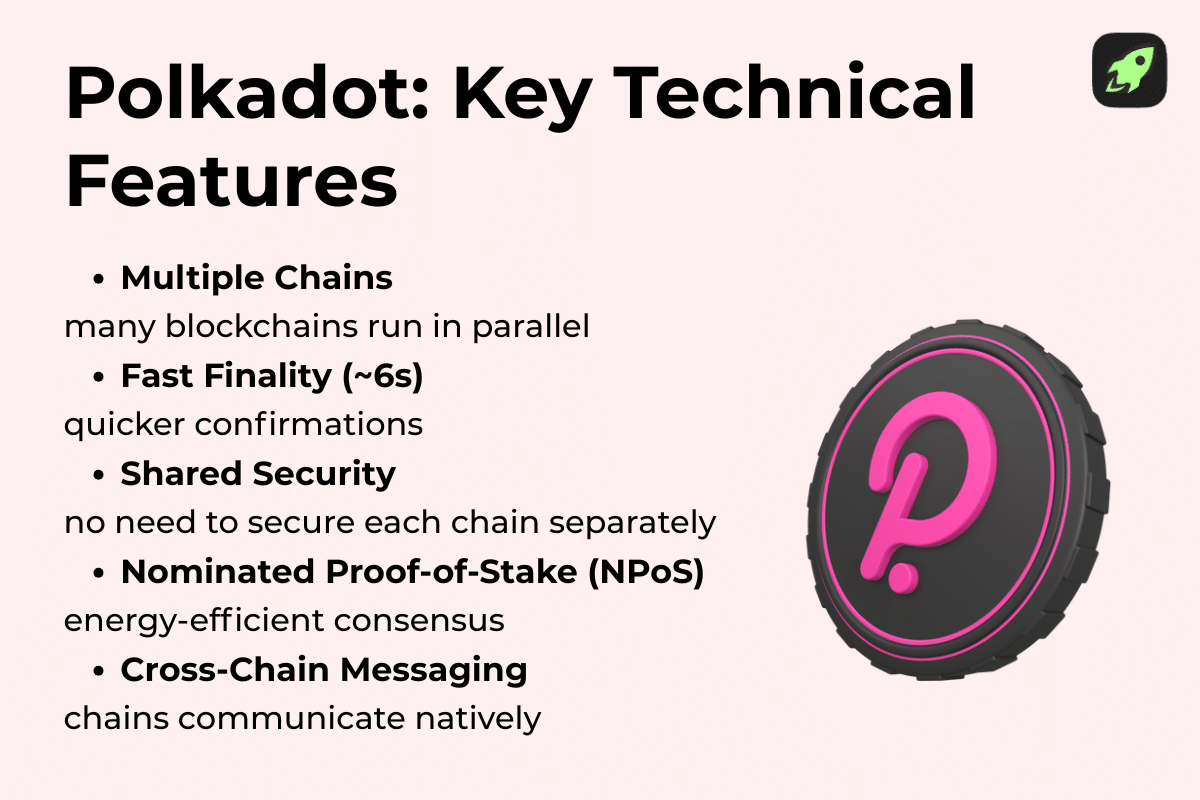
How Polkadot Works in Simple Terms
Polkadot works by splitting responsibilities across multiple layers instead of forcing one blockchain to do everything. This type of design improves efficiency and coordination.
One central chain handles security, while other chains focus on specific tasks.
Instead of processing all transactions on one chain, Polkadot spreads work across many chains. This structure reduces congestion and improves performance. It also allows different blockchains to share data safely.
At a high level, Polkadot is about allowing blockchains to specialize while staying connected: each part of the system has a clear role.
Relay Chain
The Relay Chain is the core of the Polkadot protocol. It does not run apps or smart contracts. Its main job is coordination and security.
The Relay Chain validates blocks and finalizes activity across the network. Validators operate this chain and ensure rules are being followed. Because security is centralized here, other chains do not need to recruit their own large validator sets.
This design reduces duplication and keeps the overall system more efficient.
What Are Parachains and Parathreads?
Parachains are independent blockchains connected to Polkadot. They are often described as own blockchains or independent blockchains. Each parachain can have its own logic, tokens, and use cases.
Polkadot enables independent blockchains to focus on one purpose. Some handle DeFi, others identity, gaming, or privacy. This multitude of chains exists side by side. Polkadot also has common-good parachains that provide shared services for the ecosystem.
Access to the network is limited through parachain slots, which are leased for a fixed time. Parathreads follow the same model but pay per-use instead of holding a slot.
Participants in Polkadot’s Blockchain Network
Several roles keep the system running:
- Token holders participate in governance and staking.
- Nominators support trustworthy validators by backing them with stake.
- Validators produce blocks and secure the network.
- Users interact with apps built on parachains without dealing with the base layer directly.
Each role has clear incentives. This balance keeps the Polkadot network stable and decentralized.
Polkadot’s Consensus Mechanism
Polkadot uses nominated proof-of-stake (NPoS) to secure the network. This system rewards honest behavior and punishes attacks: it is designed to balance security and decentralization.
In NPoS, validators produce blocks and secure the network. Nominators support validators by staking DOT tokens behind them. You do not need to run a node to participate. When you stake or delegate staking your DOT tokens, you help decide which validators are trusted. Poor behavior leads to penalties. Good performance earns rewards.
Read more about nominated proof-of-stake in our dedicated article: What is NPoS?
This model creates shared security. All connected chains benefit from the same secure validator set instead of protecting themselves separately, like on solochains.
How Polkadot Bridges Connect to Other Blockchains
Bridges are tools that let Polkadot connect with blockchains outside its own network, such as Ethereum. They allow assets and messages to move between otherwise separate systems. When you use a bridge, tokens are locked on one chain and represented on another. This process keeps supply consistent and prevents double spending.
In Polkadot, bridges are built to match the network’s security model. Some are fully decentralized, while others rely on trusted components.
This setup extends interoperability beyond Polkadot itself, letting you move value and data across different blockchain ecosystems safely.
History of Polkadot
| Date | Event | Details |
| 2016 | Whitepaper published | Polkadot was co-founded by Gavin Wood, Ethereum co-founder, alongside Robert Habermeier, Peter Czaban, and Jutta Steiner. Gavin Wood publishes the Polkadot whitepaper in Zug, outlining the concepts of the Relay Chain and parachains. |
| October 2017 | Initial Coin Offering (ICO) | Web3 Foundation, established by Gavin Wood, Peter Czaban, Aeron Buchanan, Reto Trinkler, and Mathias Bucher, raises 485,331 ETH (≈ $140–145M) in a public DOT token sale. |
| November 2017 | Parity multisig wallet freeze | Parity Technologies suffers a multisig wallet bug, freezing ~$150M in ETH, including funds linked to Web3 Foundation. |
| 2018 | Substrate unveiled | Parity Technologies launches Substrate, a modular blockchain framework later used as the foundation of the Polkadot SDK. |
| August 2019 | Kusama announced | Kusama, Polkadot’s canary network, is announced by Web3 Foundation and Parity Technologies, initially running on proof-of-authority. |
| October 28, 2019 | Kusama switches to NPoS | Kusama transitions from proof-of-authority to nominated proof-of-stake (NPoS), testing Polkadot’s economic and governance model in production. |
| May 26, 2020 | Polkadot mainnet genesis | Polkadot mainnet launches under proof-of-authority, with control temporarily held via a Sudo key managed by Web3 Foundation. |
| June 2020 | NPoS activated | Nominated proof-of-stake goes live on Polkadot. Validators begin securing the network and staking becomes active. |
| July 2020 | Sudo key removed | On-chain governance replaces centralized control. DOT token holders gain full governance authority through voting. |
| August 18, 2020 | DOT transfers enabled | DOT becomes transferable between accounts, enabling open market activity. |
| August 21, 2020 | DOT redenomination | DOT supply is split 100:1, reducing the unit price while keeping total market capitalization unchanged. |
| July 2020 | Private BTC sale | Web3 Foundation raises 3,982 BTC (~$43M at the time) via a private token sale to offset funds lost in the 2017 freeze. |
| Mid-2021 | Kusama parachain auctions | Kusama runs its first parachain slot auctions and crowdloans, locking millions of DOT and KSM. |
| November–December 2021 | Polkadot parachain auctions | First Polkadot auctions take place. On Dec 18, 2021, the first five parachains go live: Acala, Moonbeam, Astar, Parallel Finance, and Clover. |
| May 2022 | XCM messaging live | Cross-Consensus Messaging (XCM) launches, enabling secure communication between parachains. |
| November 2022 | DOT legal stance | Web3 Foundation states DOT is “software, not a security” following discussions with the US SEC. |
| June 15, 2023 | OpenGov launched | OpenGov replaces the original governance system, introducing track-based, parallel decision-making. |
| July 2023 | Polkadot 1.0 complete | The “Polkadot 1.0” milestone is reached. Runtime stewardship shifts to the Polkadot Fellowship. |
| April 29, 2024 | Snowbridge mainnet | Snowbridge, a trust-minimized Ethereum  Polkadot bridge, goes live. Polkadot bridge, goes live. |
| May 2024 | Asynchronous Backing | Async Backing upgrade reduces block times from ~12 seconds to ~6 seconds and increases throughput. |
| September 19, 2024 | Agile Coretime | Agile Coretime replaces long slot auctions with a flexible, on-demand parachain coretime marketplace. |
| December 4, 2024 | Kusama “Spammening” | Network stress test reaches ~143,000 TPS at ~23% capacity, showcasing scalability limits. |
| May 2025 | Runtime v1.5.0 | Elastic Scaling is targeted for enactment, enabling dynamic allocation of network cores. |
| 2024–2025 | JAM development | Join-Accumulate Machine (JAM) graypaper matures, with early testnets exploring Polkadot’s next-generation design. |
Polkadot (DOT) Token Explained
The DOT token is the core utility asset of the Polkadot network. Unlike many crypto assets, DOT tokens are not just used for payments. These tokens play an active role in how the network runs, upgrades, and stays secure.
DOT balances are measured in Planck, the network’s smallest unit.
What DOT Is Used For
DOT has several built-in functions.
It’s used to power basic network activity. You use DOT to pay for transactions, access services, and support how data moves across the network.
It also acts as a utility asset for parachains. Projects rely on DOT to operate and interact with Polkadot’s shared infrastructure.
In short, DOT is the fuel that keeps the system functional.
Governance and Voting Rights
DOT gives you a direct voice in how Polkadot evolves. Through on-chain governance, token holders can vote on upgrades, fixes, and policy changes. Each referendum passes through lead-in, decision, and confirmation phases.
Your voting power depends on how much DOT you hold and how long you commit it. This system removes the need for off-chain decision-making.
If you own DOT, you can influence real protocol changes.
Staking DOT for Rewards
You can stake DOT to help secure the network and earn rewards. Staking locks your tokens and puts them to work. Nomination pools let smaller holders participate in staking collectively.
When you stake or delegate staking DOT tokens, you support reliable validators. In return, you receive the rewards paid in DOT.
This system encourages long-term participation instead of short-term trading.
Bonding DOT to Connect Parachains
DOT is also used for bonding, which allows new parachains to connect to Polkadot. Projects must lock DOT as collateral to access parachain slots. Bonding prevents spam and ensures only committed projects join the network. Once the lease ends, bonded DOT is returned.
This mechanism keeps network resources scarce and valuable.

How to Get Free Crypto
Simple tricks to build a profitable portfolio at zero cost

Why People Invest in Polkadot
People invest in Polkadot because it targets a real technical problem: blockchains do not work well together. Polkadot focuses on interoperability, shared security, and scalability from day one. And this leads to the other reason people invest—its long-term design. Polkadot itself is built as evolving infrastructure, not a single finished project.
Some investors also look at its governance. Holding DOT gives you voting power, not just exposure to price.
That said, Polkadot is still a growth-stage network. Its value depends on adoption and execution. Still, if you believe in a multi-chain future, Polkadot fits that thesis.
Real-World Uses and Projects
Polkadot already supports real blockchain projects with clear use cases.
- For smart contracts, Moonbeam lets developers run Ethereum-compatible apps while using Polkadot’s shared security. This lowers the barrier to entry for teams migrating from Ethereum.
- In DeFi, Acala focuses on lending, staking, and stablecoin infrastructure built directly into the network.
- For digital identity, Polkadot originally supported KILT Protocol, which pioneered self-sovereign credentials on-chain. That project has since evolved into Primer, now operating via primer.systems, while continuing to build on the same identity foundations.
- Other parachains target gaming, NFTs, and data services. Cross-chain tools like Snowbridge extend this further by connecting Polkadot apps directly to Ethereum.
The pattern stays the same: each chain does one job well, and Polkadot lets them work together.
Risks and Challenges of Polkadot
Polkadot’s network is complex by design. Multiple chains, roles, and rules make it harder to understand than a single blockchain. For new users, concepts like parachains, staking roles, and governance tracks add a definite learning curve.
Adoption is arguably the biggest challenge. Polkadot’s future depends on developers choosing to build and stay, all while competing ecosystems like Ethereum and its Layer 2 networks fight for the same talent and users.
There are also technical risks. Bugs, delayed upgrades, or poorly maintained parachains can affect trust. While shared security reduces some risks, it does not eliminate them.
Finally, Polkadot is still evolving. Major features continue to roll out, and Polkadot actively uses test networks like Westend and Paseo to trial upgrades. Its long-term future depends on execution, real usage, and sustained developer activity, not promises.
How Has DOT’s Price Changed Since Its Launch?
Since its launch in 2020, DOT’s price has moved with the broader cryptocurrency market and its own development events. Polkadot reached its all-time high (ATH) near $55 per DOT on November 4, 2021, during the peak of the 2021 crypto bull market. Since then, the price has fallen sharply—by around 96% from its peak—as markets cooled and speculative demand faded.
Through 2022–2024, DOT generally trended lower with broader market volatility, often reflecting sentiment more than network milestones. For example, after upgrades in mid-2024, prices remained subdued, showing that technical progress doesn’t always immediately translate to price gains.
The all-time low occurred in late 2025, with DOT trading below $2 at times, reflecting macro weakness and liquidations in risk assets.
Overall, DOT’s price history tells a familiar story in crypto: early rapid gains, a big peak with the 2021 boom, and a multi-year correction that has kept prices far below ATH levels. You can take a closer look at DOT’s future in our DOT price prediction.
Is Polkadot a Good Investment?
It may be a good long-term investment, but only if you accept high risk. Polkadot is still building core infrastructure, not chasing short-term hype.
At the time of writing in early 2026, DOT trades far below its past highs after hitting an all-time low. This phase followed a long market downturn and heavy selling of DOT tokens.
For patient investors, this can look like a recovery setup. For others, volatility remains a serious factor.
Where Do I Buy Polkadot (DOT)?
You can buy DOT through many online platforms.
Changelly lets you purchase Polkadot using 20 local payment methods, including cards and bank transfers. Transactions process fast, and you can receive DOT directly in your wallet. This setup suits beginners who want quick access without complex trading interfaces.
Final Thoughts
Polkadot is a solid project built for a multi-chain future. It focuses on coordination, shared security, and flexibility instead of one chain doing everything. This is why its success depends on adoption, execution, and long-term usage even more than other projects.
FAQ
Why does Polkadot need both a Relay Chain and parachains?
They play different roles. Polkadot splits tasks to stay efficient: The Relay Chain handles security and coordination, while parachains focus on specific functions like DeFi or identity. This separation reduces congestion and lets each chain specialize without sacrificing shared security.
Can Polkadot be used for NFTs, gaming, or DeFi?
Yes. Polkadot already supports all three. The key point is separation. Games don’t compete with finance apps for block space.
What kinds of projects or dApps are currently running on Polkadot parachains?
Polkadot hosts a wide range of blockchain projects, each built for a specific purpose.
For smart contracts, Moonbeam and Astar let developers run Ethereum-style and WebAssembly apps.
In DeFi, Acala, Parallel Finance, and HydraDX focus on lending, liquidity, and trading.
NFT, gaming, and identity projects like Efinity, Mythical Games, and KILT also show how specialized chains can scale without competing for block space.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.
The post What Is Polkadot (DOT)? The Blockchain That Connects Blockchains appeared first on Cryptocurrency News & Trading Tips – Crypto Blog by Changelly.
Cryptocurrency News & Trading Tips – Crypto Blog by Changelly



















